Adaptive Mesh Refinement by Air Shaper
- contributor: Nikola Majksner and Wouter Remmerie
- affiliation: AirShaper
- contact: click here for email address, click here for email address
- OpenFOAM versions: v2206
- Published under: CC BY-NC-ND license (creative commons licenses)
Go back to Collection by authors.
Go back to Meshing.
Contents
Adaptive Mesh Refinement
OpenFOAM motorBike case with adaptive volume & surface mesh refinement based on curl(U) or grad(p)
Description
This repository provides adaptive mesh refinement for both the volume mesh and the surface mesh. Any field can be used for refinement. In this tutorial, two options have been included:
- grad(p): the pressure gradient
curl(U): the curl of the velocity field
Both are multipled by the cell length to “discourage” the algorithm to keep refining the smallest cells. The method has 3 major parts:
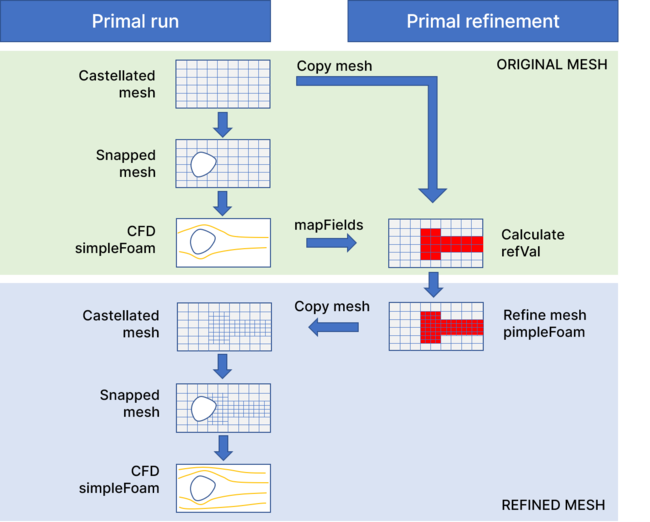
Initial mesh
SnappyHexMesh is run in two separate steps:
- castellated mesh: only runs the refinement phase using “baffles” for the surface of the geometry (to avoid the mesh inside the geometry being cut and to keep all cells hexagonal). This mesh is stored in
primal_refinementfor use in the mesh refinement phase. - snapping phase: this part will cut the mesh (by also having castellated enabled) and snap it to the surface (by setting the surface patch type to
wall). This mesh is used inprimal_runfor the first CFD loop.
- castellated mesh: only runs the refinement phase using “baffles” for the surface of the geometry (to avoid the mesh inside the geometry being cut and to keep all cells hexagonal). This mesh is stored in
Refinement field
Once the first CFD loop has finished, it maps the fields onto the stored castellated mesh (in
primal_refinement) and calculates the refinement field (refVal), for which the lower limit value should be set manually inprimal_refinement/constant/dynamicMeshDict.Mesh refinement
The refinement is then applied to the castellated mesh of the first loop. Once refinement is done, the castellated mesh is copied to
primal_runwhere the snapping phase is executed again to snap the refined mesh to the surface. This mesh is then used for the second and final CFD run.
Conclusions
This method allows for mesh refinement of both the volume and the surface mesh.
In contrast to other OpenFOAM® based methods that refine on the surface, the mesh is re-snapped after refinement, which improves the correspondence to the real geometry.
Adaptive mesh refinement can greatly reduce the computational cost, as the mesh is applied in a more efficient way.
Any given field can be created to steer the mesh refinement. The gradient of pressure (useful for airfoils for example) and curl of the velocity field (useful for wake refinement for example) have been included.
We definitely welcome any contribution to further improve this method (for example, would it be easier to just use refineMesh instead of pimpleFoam?).
How to run the case
- Make sure you have installed latest OpenFOAM v2012
- Clone this repository on your machine
git clone https://github.com/airshaper/adaptive-mesh-refinement.git - Adopt
primal_run/system/decomposeParDictdepending on number of cores you have. ChangenumberOfSubdomains 6to number of cores or threads you have available. Also modifynundercoeffsto reflectnumberOfSubdomainschange. For example if you have 12 cores yournshould be(3 2 2)if you have 16 cores for example thennshould be(4 2 2)and so on. - Go to
cd ./primal_runthen run./Allrun
Results
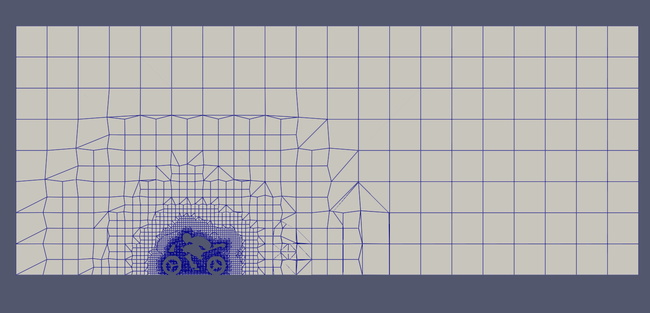
Non-refined mesh slice
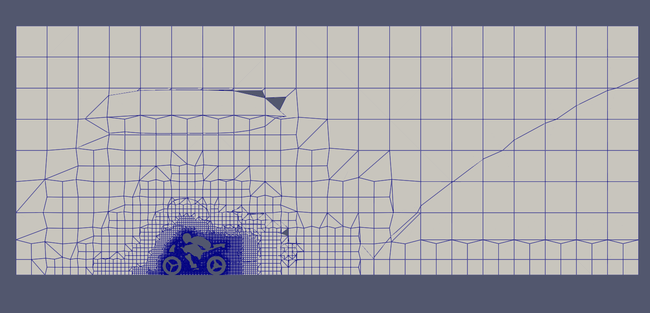
Refined mesh slice with curl(U) (notice how curl(U) refines the wake as well)
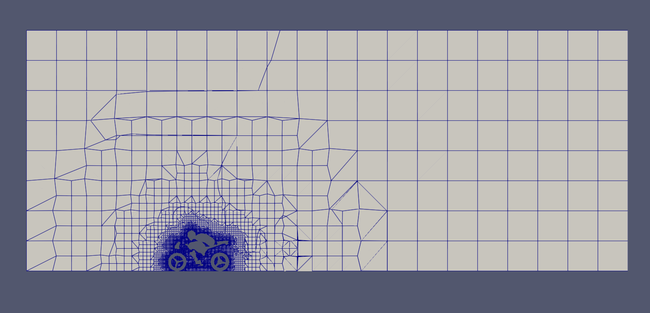
Refined mesh slice with grad(p) (notice how grad(p) mostly refines the surface)
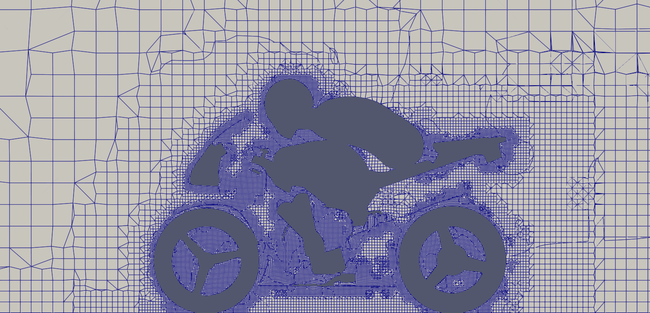
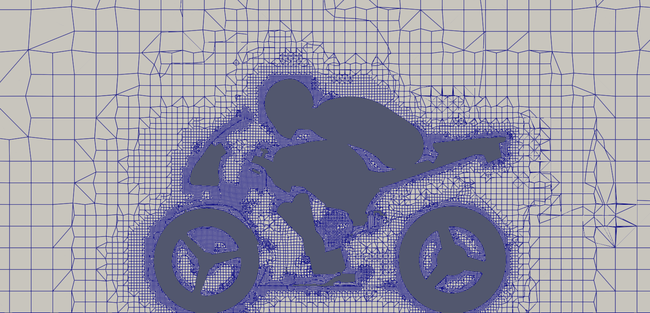
Zoomed Non-refined mesh slice
Zoomed Refined mesh slice with curl(U)
Zoomed Refined mesh slice with grad(p)
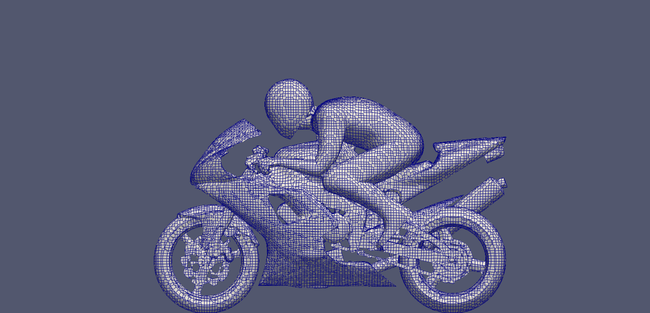
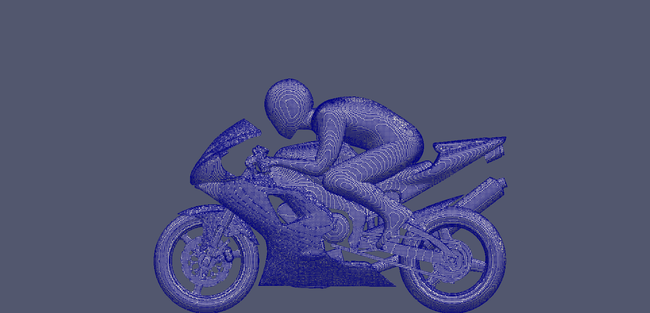
Non-refined surface mesh
Refined surface mesh based on curl(U)
Refined surface mesh based on grad(p)
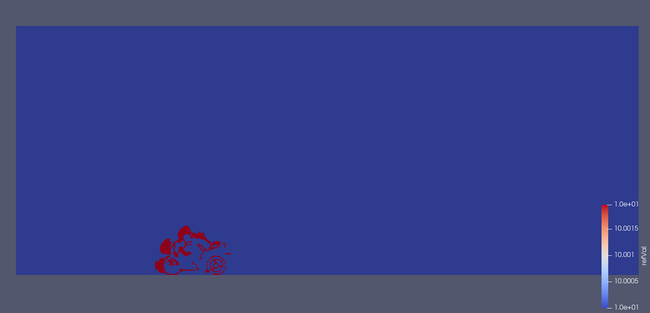
Custom calculated field refVal based on curl(U)
Custom calculated field refVal based on grad(p)